Description
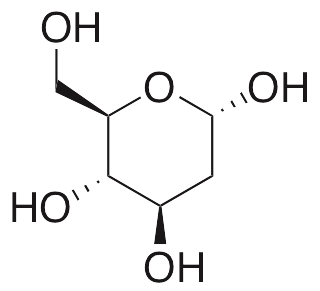
2-deoxy-D-glucose inhibits glucose metabolism and is used as a biomarker of glucose metabolism, hypoxia, and angiogenesis in a variety of models and cell types, including neurotoxicity, cancer, and autoimmune disease; the 2-OH group of glucose is replaced by a hydrogen and therefore this compound can not be metabolized properly. 2-deoxy-D-glucose inhibits N-linked glycosylation and glycolysis, inhibiting surface expression of MICA/B and other NKG2D ligands on cells. This compound also exhibits anticancer and pro-oxidative activities, increasing oxidative stress and mimicking glucose deprivation, resulting in cell death of cancer cells.