Description
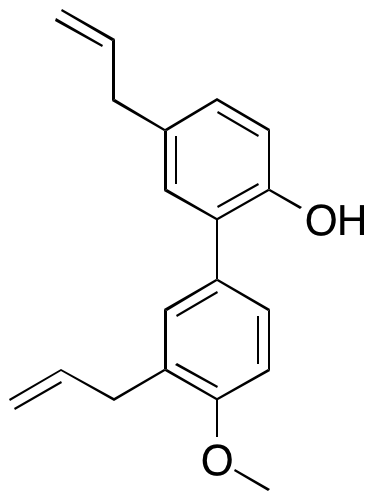
4-O-Methylhonokiol is a major bioactive constituent of Magnolia officinalis stem bark. In a study with C57BK/6J mice, 4-O-methylhonokiol prevented high-fat-diet induced obesity and insulin resistance, in addition to restoring impaired cardiac insulin signaling. In another study using female RjOrl mice, 4-O-methylhonokiol was shown to act as a central nervous system penetrating substrate-specific inhibitor of COX-2 and as a CB2 receptor agonist. Furthermore, in high-risk HPV-16 genotype SiHa cells, treatment with 4-O-methylhonokiol suppressed the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway thereby reducing the survival of the cells. 4-O-methylhonokiol has also shown several other biological activities including anti-inflammatory, antithrombotic, anti-anxiety, antimicrobial, and anti-HIV activities.