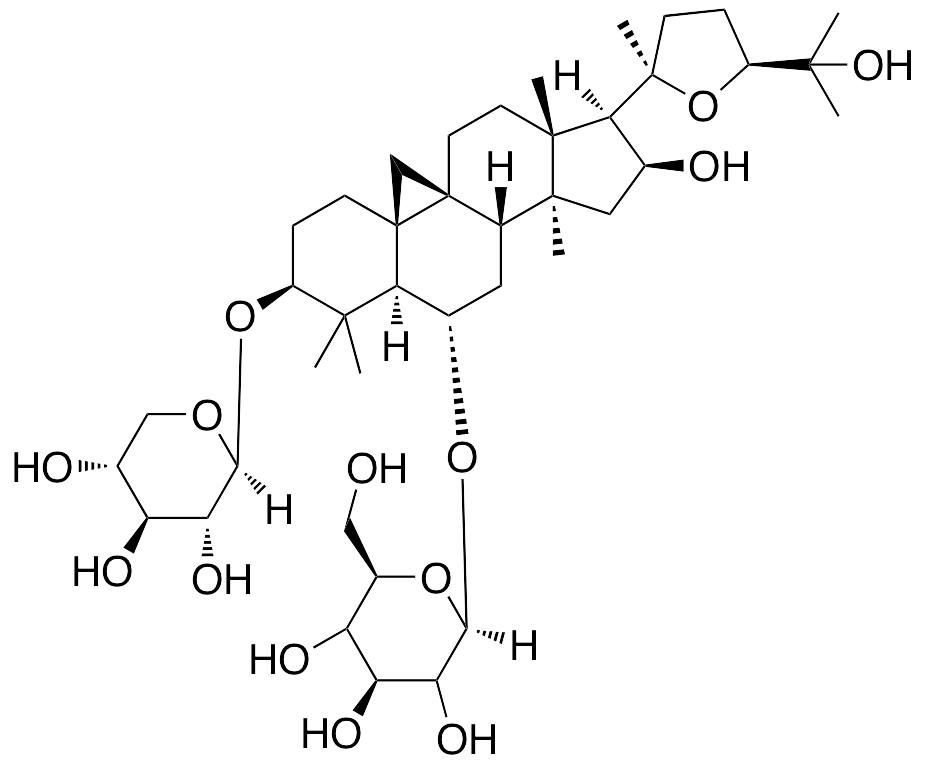
Description
Astragaloside IV is an active compound found in Astragalus membranaceus that exhibits cardioprotective, antioxidative, and pro-angiogenic activities. Astragaloside IV prevents LPS-induced increases in Ca2+, activation of CaN and GATA-4, and nuclear factor of activated T cells 3 (NFAT3) translocation, inhibiting cardiac hypertrophy. Additionally, astragaloside IV decreases expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) and prevents ischemia/reperfusion-induced myocardial infarction and myocardial apoptosis in animal models. In other animals, astragaloside IV prevented increases in ROS, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and downregulation of superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione, and tau phosphorylation induced by experimental autoimmune encephalitis (EAE); this compound also prevents related decreases in the Bcl-2/Bax ratio and changes in T cell differentiation and migration. In endothelial cells, astragaloside IV activates JAK/STAT and ERK 1/2 signaling and upregulates production of eNOS and NO, promoting tube/vessel formation.