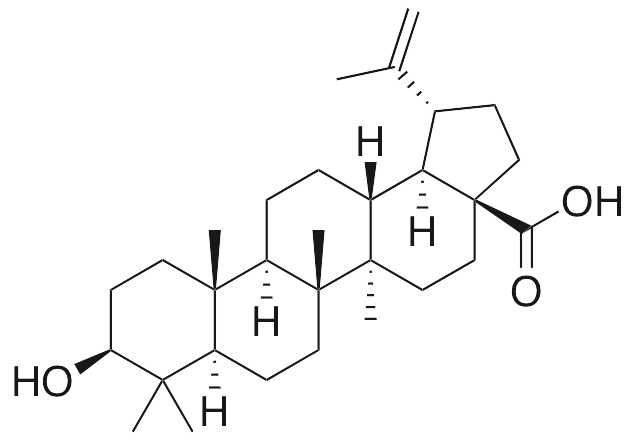
Description
Betulinic acid is a pentacyclic triterpene that exhibits antithrombotic, anti-atherosclerotic, antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, anti-angiogenic, and anticancer chemotherapeutic properties. Betulinic acid decreases expression of P-selectin and binding of PAC-1, preventing platelet aggregation. In macrophages, betulinic acid inhibits phosphorylation of IκB and p65 and prevents activation of NF-κB, promoting cholesterol efflux and decreasing cellular levels of cholesterol; in vivo, this leads to a decrease in atherosclerotic lesion size. In rat aortic tissue, betulinic acid induced relaxation through preventing increases in ROS, decreases in NO, and decreases in eNOS and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity induced by superoxide anions. In animal models, this compound increases activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase, and glutathione reductase and also decreases expression of cyclooxygenase (COX-2), NO, TNF-α, and IL-1β, resulting in a decrease in paw edema. In adenocarcinoma cells, this betulinic acid inhibits collagen biosynthesis, decreases prolidase activity, and decreases expression of HIF-1α, VEGF, and α1/2 integrins. Betulinic acid decreases expression of cyclin D3 and Bcl-xl in vitro, inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Additionally, this compound downregulates expression of Sp1 protein, decreasing lung tumor growth in animal models.