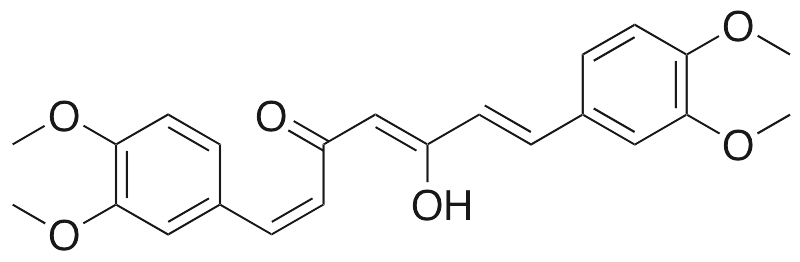
Description
Like its parent compound, curcumin, this curcuminoid exhibits anticancer, antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial activities. In breast cancer cells, dimethoxycurcumin alters mitochondrial membrane potential, decreases ATP synthase activity, and induces DNA damage and apoptosis. In comparison to curcumin, dimethoxycurcumin is more stable and displays greater apoptosis-inducing activity in vitro. Additionally, dimethoxycurcumin is more effective in inhibition of NO production, iNOS expression, and NF-κB activation than curcumin. Dimethoxycurcumin exhibits pro-oxidative activity in cancer cells, increasing reactive oxygen species (ROS), but does not do so in normal cultured cells. This compound also inhibits the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-2, IL-6, and IFN-γ in vitro. Dimethoxycurcumin has phototoxic antibacterial activity against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria and binds the minor groove of DNA without intercalation.