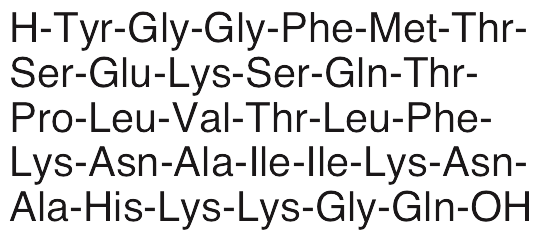Description
β-Endorphin is an endogenous opioid peptide that acts as an agonist at μ-opioid receptors (μORs) and exhibits immunomodulatory, neuromodulatory, antidepressant, and antinociceptive/analgesic activities. In vivo, β-endorphin increases levels of B-cells and production of antibodies as well as secretion of IL-4 and proliferation of spleenocytes, shifting the immune response toward Th2-specific mediators. This peptide, like other endogenous opioids, plays a significant role in reward and reinforcement signaling, especially in brain regions such as the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and nucleus accumbens (NAcc). β-Endorphin release is induced during exercise and shows antidepressant activity in clinical studies.