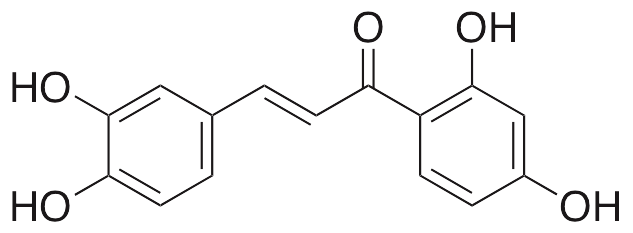
Description
Butein is a flavonoid originally found in the bark of Rhus verniciflua and the flowers of Butea monosperma. Butein exhibits anticancer chemotherapeutic, anti-angiogenic, neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, and anti-fibrotic activities. In lung cancer cells, butein decreases expression of COX-2, inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis; this compound also inhibits tumor growth of prostate cancer xenografts in vivo. Butein inhibits phosphorylation of Akt, mTOR, and their downstream targets and suppresses VEGF-induced cell proliferation, migration, and tube formation in endothelial progenitor cells; it also inhibits vessel sprouting from aortic rings in vivo. In animal models of spinal cord injury, butein decreases expression of NF-κB and IκBα, inhibits activation of caspase 3, and suppresses infiltration of neutrophils. In cellular models, this compound increases levels of glutathione and activity of catalase and glutathione S-transferase and decreases levels of lactate dehydrogenase. It also acts as a free radical scavenger. Additionally, it prevents hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation, downregulating expression of TGF-β, TIMP-1/2, and MMP-2 and inhibiting activation of NF-κB, p38, JNK, and Smad3.