Description
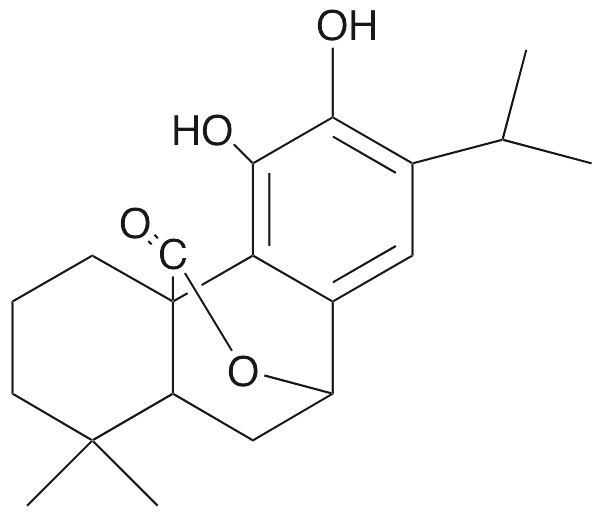
Carnosol is a diterpene compound originally found in rosemary plants. Carnosol exhibits antidepressant, anti-inflammatory, anti-angiogenic, and anticancer chemotherapeutic activities. Carnosol inhibits microsomal prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) synthase and decreases production of pro-inflammatory PGE2; in vivo, it inhibits PMA-induced edema and decreases expression of IL-1β and TNF-α. Carnosol inhibits the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in ovarian cancer cells and decreases growth and viability in breast, ovarian, and intestinal cancer cells. In colon cancer cells, carnosol increases activation of caspases 3 and 9, induces cleavage of PARP, upregulates expression of p53, downregulates expression of MDM2, and suppresses activation of STAT3, JAK2, and Src. Additionally, this compound inhibits androgen and estrogen receptors, suppressing tumor growth and PSA levels in animal models of prostate cancer.