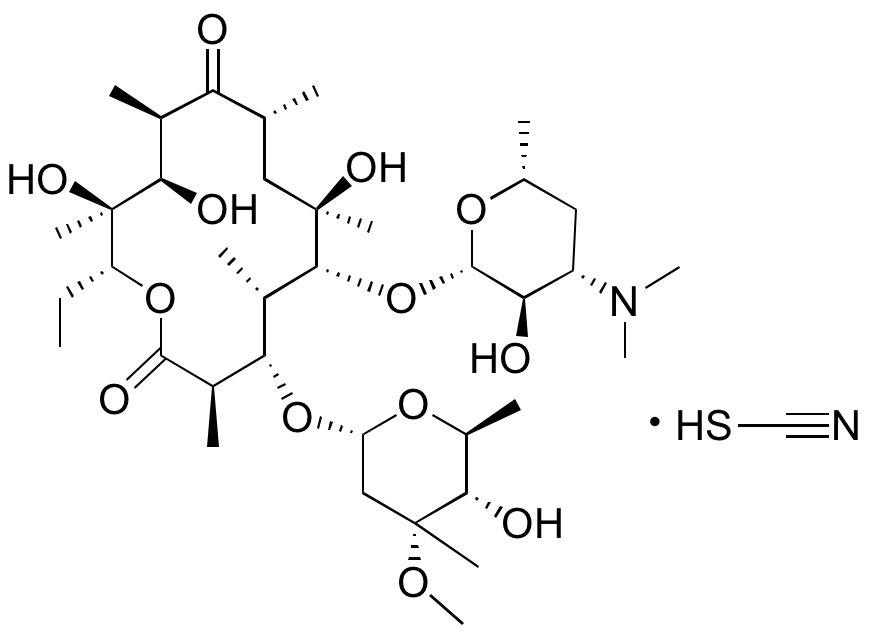
Description
Erythromycin is a macrolide antibiotic that binds the 50s subunit of bacterial ribosomes, inhibiting protein synthesis by preventing transfer of tRNA from the A site to the P site. This compound displays antibacterial activity against both gram positive and gram negative bacteria; it also inhibits mammalian mRNA splicing.