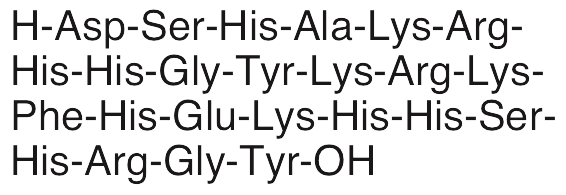Description
Histatin 5 is an endogenous antimicrobial peptide (AMP) present in the salivary gland. Histatin 5 exhibits anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and antifungal activities. In myeloid dendritic cells, histatin 5 binds Poryphyromonas hemagglutinin B, inhibiting production of MIP-1α, MIP-1β, and TNF-α. Histatin binds bacterial DNA, displaying bactericidal activity against gram positive bacteria such as Streptococcus. Additionally, histatin 5 causes ion flux-induced cell death of Candida cells in an ex vivo model of oral candidiasis.