Description
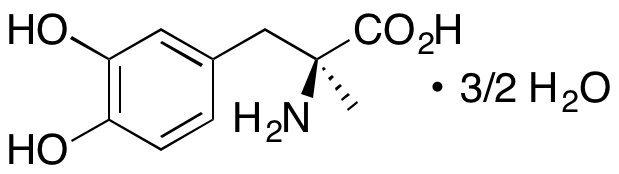
Methyldopa exhibits antihypertensive and sedative activities. In circulation, methyldopa is metabolized to α-methylnorepinephrine by dopamine β-hydroxylase, which activates α2-adrenergic receptors, acting as a sympatholytic and inhibiting the sympathetic nervous system. This compound also inhibits DOPA decarboxylase, decreasing production of dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. In animal models, methyldopa exhibits NO-dependent sedative activity similar to that of clonidine.