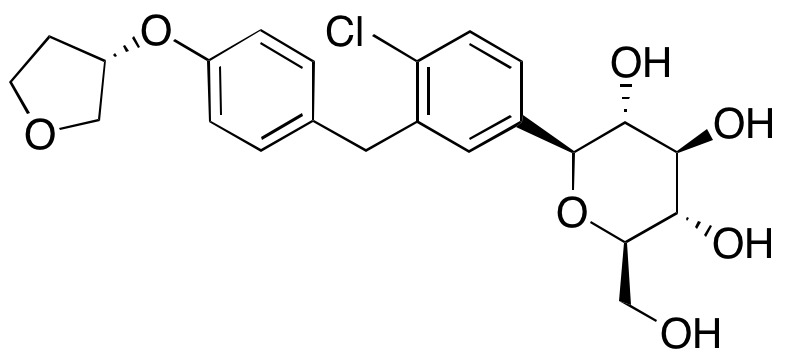
Description
Empagliflozin is a sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor. Chronic treatment of Zucker diabetic fatty rats with empagliflozin was able to prevent the development of oxidative stress, AGE/RAGE signaling and inflammation, and to partially improve endothelial function. High-dose treatment of C57BL/6J mice with empagliflozin resulted in suppressed weight gain in addition to ameliorating glucose intolerance and insulin resistance. Empagliflozin treatment also protected mice from diet-induced hepatic steatosis and inflammation, decreased M1 macrophages, and increased M2 macrophages. Additionally, empagliflozin treatment lowered blood glucose levels, improved cardiac function, improved histopathalogic changes in the myocardium, and inhibited cardiomyocyte apoptosis by down-regulating expression of CHOP and GRP8 and inactivating caspase-12 in diabetic cardiomyopathy rats.