Description
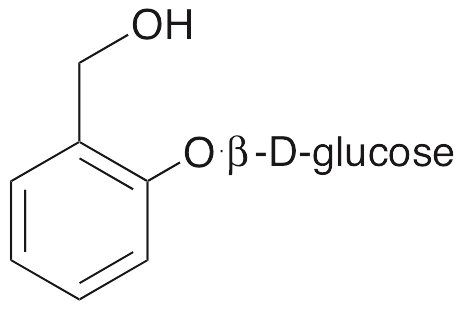
Salicin is an alcoholic β-glucoside originally found in the bark of the white willow tree; it exhibits anticancer chemotherapeutic, anti-angiogenic, anti-inflammatory, and antithrombotic activities. Salicin decreases production of ROS and VEGF, suppresses activation of ERK, and inhibits migration, tube formation, and sprouting in endothelial cells; in cancer models, salicin inhibits tumor growth. Salicin also inhibits dextran-induced colitis in animal models, preventing shortening of colon length, suppressing release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and decreasing activity of myeloperoxidase. This compound also inhibits serine proteases such as thrombin.