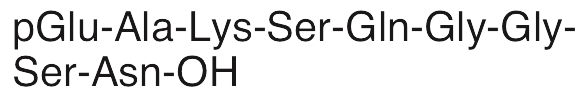Description
Serum thymic factor (FTS) is a synthetic nonapeptide hormone that exhibits anti-apoptotic, anti-diabetic, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory activities. In vivo, FTS increases activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and decreases activation of ERK, inhibiting cephaloridine-induced kidney damage and dysfunction. In other animal models, FTS increases expression of Bcl-2 and IL-6, preventing LPS-induced damage to pancreatic cells. FTS also suppresses the symptoms of experimental autoimmune encephalitis (EAE) in animal models. In vitro, this peptide increases T cell differentiation and activates T cells and NK cells. In vivo, FTS prevents the viral induction of diabetes, preventing loss of insulin granules, myocardial inflammation, and pancreatic islet cell necrosis.