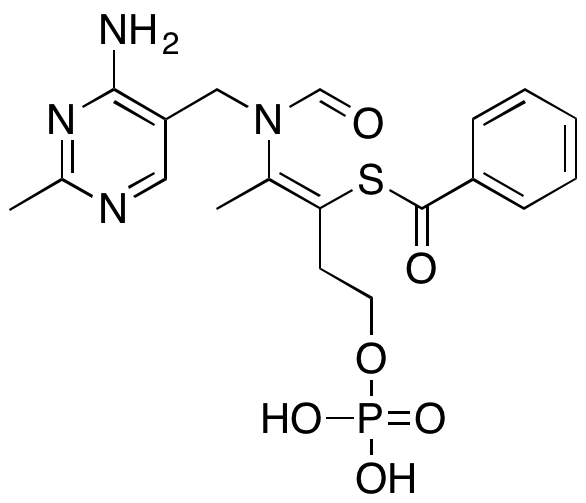
Description
Benfotiamine is a synthetic, lipid-soluble derivative of the B vitamin thiamine. Benfotiamine exhibits antinociceptive, neuroprotective, and anti-inflammatory activities. In animal models, benfotiamine inhibits pain signaling in a prostatic acid phosphatase-dependent manner. In vitro, benfotiamine decreases production of amyloid-β (Aβ) and downregulates activity of glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3). In macrophages, this compound inhibits LPS-induced activation of phospholipase A2 (PLA2), release of leukotrienes, prostaglandins, and thromboxane B2 (TxB2), and also suppresses oxidative stress. Benfotiamine also decreases oxidative stress induced by streptozocin in animal models.