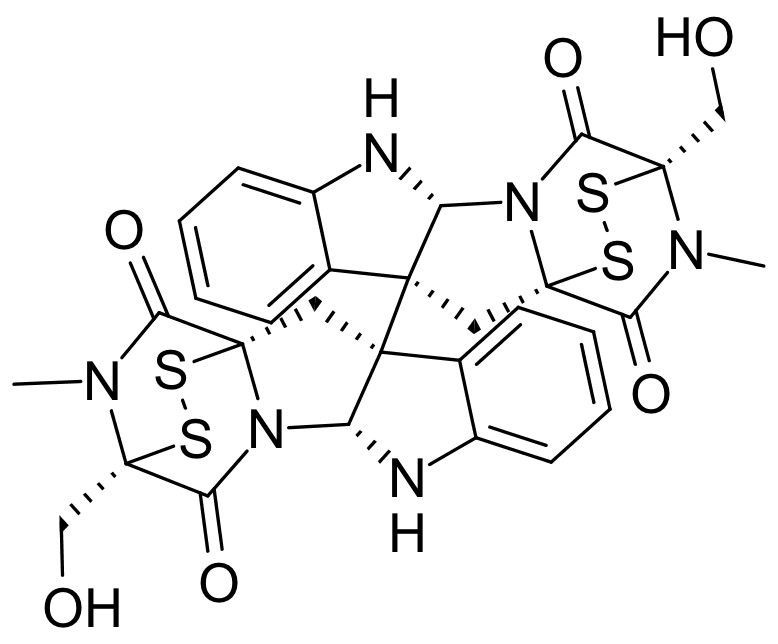
Description
Chaetocin is naturally produced by Chaetomium species fungi. In human melanoma cells, treatment with chaetocin suppressed proliferation, induced apoptosis, and increased the level of reactive oxygen species. In Epstein-Barr virus cells, it apparently up-regulated lytic transcription and DNA replication via the ROS pathways. In a rat model of chronic heart failure, treatment prolonged survival and restored mitochondrial dysfunction. Using NCI-60 screening found chaetocin to inhibit proliferation in all tested solid tumor cells even more so than multiple myeloma cells. It was also observed to cause a 25-fold induction of latent HIV-1 expression which may be an effective way to purge cells of latent HIV-1.