Description
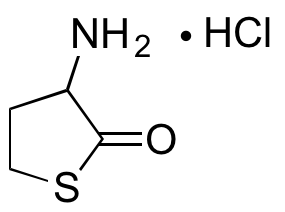
D,L-Homocysteine thiolactone binds to and induces conformational changes in various plasma proteins. This compound slows coagulation and causes more tightly packed fibrin structure formation; it is detrimental to vascular function and may induce oxidative stress. D,L-Homocysteine thiolactone exhibits cardiomodulatory, epileptogenic, and neurotoxic activities. In isolated hearts, this compound decreases left ventricular systolic blood pressure and cardiac force. In vivo, this compound induces seizures and is thought to play a role in the development of Alzheimer’s disease.