Description
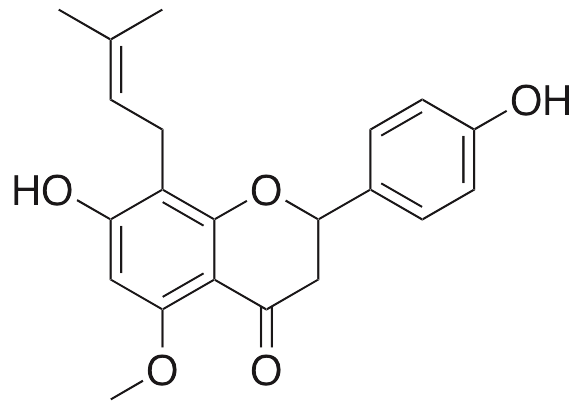
Isoxanthohumol (IX) is a prenylflavinoid and derivative of xanthohumol found in Humulus lupulus. IX, similar to xanthohumol, exhibits anti-inflammatory, anti-angiogenic, and pro-apoptotic activities, although at a lesser potency than xanthohumol. IX modulates signaling between endothelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells in a variety of cell lines, decreasing levels of TNF-α, NF-kB, VEGF-R2, and angiopoetins 1 and 2. In mature adipocytes, IX increases ROS and induces apoptosis; in preadipocytes, this compound inhibits differentiation and also induces apoptosis as exhibited by increases in cytochrome c and PARP and decreases in PPARy, adipocyte protein 2, and CEBP2 upon stimulation with IX. IX undergoes transformation in vitro and in the intestine to form 8-prenylnaringenin, a potent phytoestrogen.