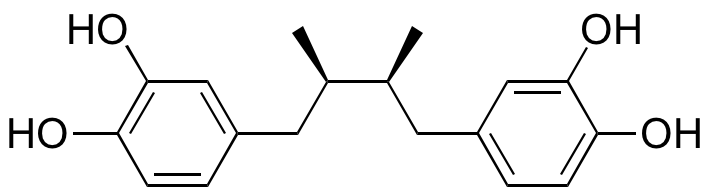
Description
Nordihydroguaiaretic acid (NDGA) is a phenol found in the creosote bush that exhibits antioxidative, antiviral, anti-angiogenic, anti-metastatic, anti-inflammatory, anti-hyperlipidemic, anti-osteoporotic, anti-aging, neuromodulatory, anti-parasitic, antifungal, and anticancer chemotherapeutic activities. NDGA scavenges ROS, inhibits 5-lipoxygenase, and activates Nrf2. This compound inhibits dengue virus replication by preventing viral assembly; it also inhibits growth of Culex and Candida. In animal models, NDGA increases overall life span and inhibits acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butylcholinesterase (BChE). In vivo, NDGA inhibits angiogenesis and suppresses invasion and proliferation of glioma cells. In various models, NDGA inhibits Ca2+ signaling and PAR2 activity, decreasing expression of IL-8, ICAM-1, IgE, and involucrin. In animal models, this compound increases expression of PPARα and decreases levels of serum triglycerides and liver weight. Additionally, NDGA inhibits osteoclastogenesis in vitro and decreases bone destruction in vivo. In cellular and animal models of breast cancer, NDGA inhibits mTORC1, decreases expression of VEGF, cyclin D1, and HIF-1α, and suppresses cellular proliferation and tumor growth.