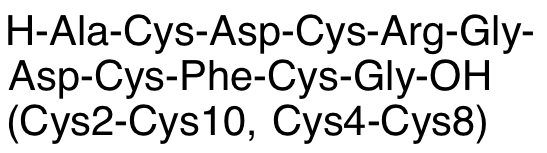Description
RGD-4C is a cell-adhesive peptide that binds αvβ3 and αvβ5 integrins; these integrins are overexpressed in many cancers and growing vessels, so RGD-4C is often attached to viral treatments to better deliver or target the treatment to cancerous tissues. RGD-4C exhibits anticancer chemotherapeutic and anti-angiogenic benefits in models of various cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), melanoma, and glioma.