Description
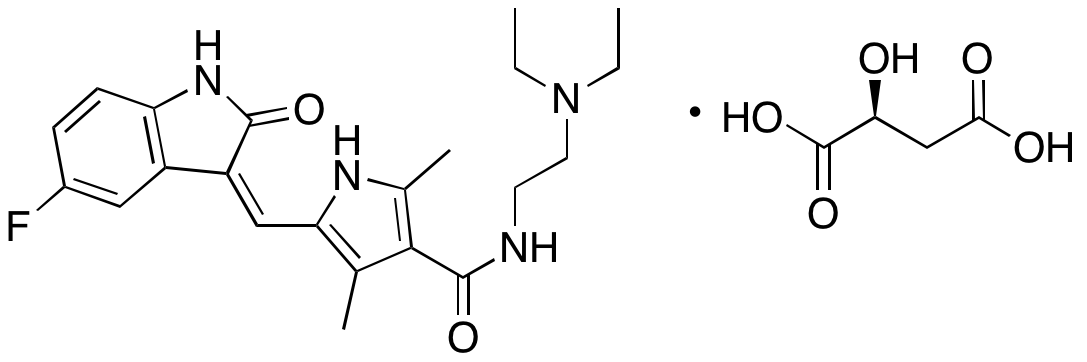
Sunitinib is an inhibitor of several tyrosine kinases, including PDGFR, VEGFR, KIT, and FLT3. Sunitinib also inhibits mTORC1 signaling. Sunitinib is currently clinically used to treat renal cell carcinoma and gastrointestinal stromal tumors, but is in clinical trials as a potential treatment for a variety of other cancers. Sunitinib exhibits anticancer chemotherapeutic, anti-angiogenic, and anti-fibrotic activities. In anaplastic thyroid cancer cells, sunitinib decreases activity of VEGFR2, prevents phosphorylation of EGFR, ERK1/2, and Akt, and suppresses expression of cyclin D1, inhibiting cell proliferation; in paired animal models, this compound inhibits tumor growth. In acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) cells, sunitinib decreases expression of cyclin D1, cyclin D3, cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2), Bcl-2, and Mcl-1 and increases expression of p27, pRb1, p130, Bax, Bak, Fas, FasL, DR4, DR5, and activated PKC, resulting in activation of caspases 2, 3, 8, and 9 and apoptosis. In endothelial cells, sunitinib inhibits tube formation and vascular sprouting. In animal models, sunitinib decreases cyst area and increases the number of cyst-free subjects, indicating potential benefit in the treatment of endometriosis. Additionally, this compound inhibits collagen synthesis, cell migration, contraction, and cell differentiation of hepatic stellate cells.