Description
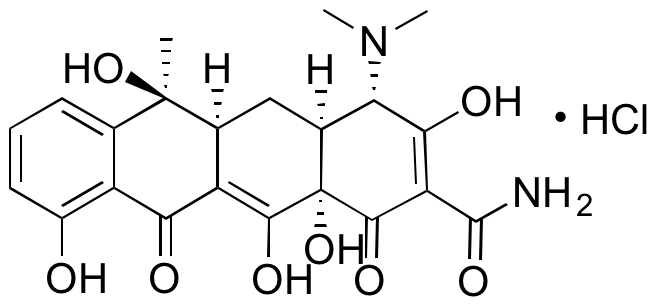
Tetracycline is a polyketide antibiotic originally produced by Streptomyces that exhibits antibacterial and neuroprotective activities. Tetracycline binds the 30S subunit of the bacterial ribosome, preventing aminoacyl-tRNA from binding to the ribosomal A site and inhibiting protein synthesis. Tetracycline is clinically used to treat acne, rosacea, Lyme disease, and various bacterial infections. Tetracycline binds amyloid-β (Aβ) peptides, increasing their solubility and decreasing their neurotoxicity in vitro. Tetracycline may also inhibit matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). Additionally, tetracycline inhibits mammalian RNA splicing.