Description
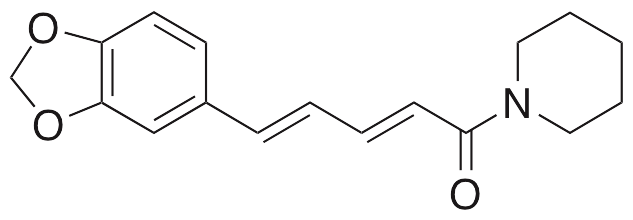
Piperine is an alkaloid originally found in several species of black and long peppers. Piperine exhibits anticancer, anti-diabetic, immunomodulatory, antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, cognition enhancing, and neuroprotective activities. In prostate cancer cells, piperine induces cell cycle arrest and autophagy by increasing levels of p21 and p27 and decreasing levels of cyclin D1 and cyclin A. In animal models, piperine decreases blood glucose levels. In LPS-treated dendritic cells, piperine inhibits expression of CD40 and CD86, suppresses production of IL-12 and TNF-α, and prevents activation of ERK and JNK. In animal models of Alzheimer’s disease, this compound improves memory impairment and neurodegeneration. In animal models of Parkinson’s disease, piperine decreases 6-OHDA-induced lipid peroxidation, decreases levels of TNF-α and IL-1β, and increases levels of glutathione, resulting in improvements in motor coordination and balance. Piperine also activates transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) channels.