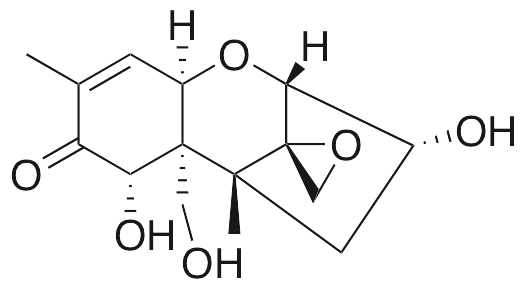
Description
Deoxynivalenol is a trichothecene mycotoxin initially produced by species of Fusarium that is found in cereals and other products of wheat or similar grains. Deoxynivalenol exhibits immunomodulatory, cytotoxic, and pro-inflammatory activities. In vivo, deoxynivalenol increases the formation of pores in the intestinal epithelial barrier of the jejunum, increases the number of CD16+ cells, and downregulates expression of syndeca, fibulin 6, and BM-40. In vitro, this toxin activates p38 MAPK and p53 to induce activation of caspases 3, 8, and 9, resulting in apoptosis; it also induces rRNA cleavage, inhibiting ribosomal translation. In other cellular models, deoxynivalenol upregulates expression of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, COX-2, and mPGES-1.