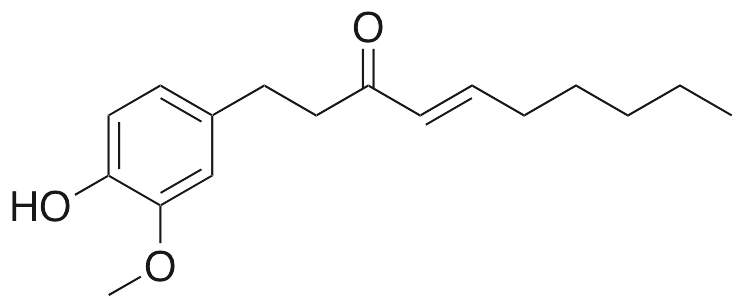
Description
Shogaol is a originally found in species of Zingiber; it exhibits antiemetic, anticancer chemotherapeutic, anti-metastatic, chemopreventive, anti-ulcerative, anti-inflammatory, anticoagulant, and antinociceptive activities. Shogaol inhibits activation of STAT3, JAK2, and c-Src, decreases expression of Bcl-xl, Bcl-2, and survivin, and increases caspase-dependent apoptosis in breast cancer and prostate cancer cells; it also inhibits tumor growth. Shogaol also inhibits invasion and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by decreasing expression of matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 (MMP2/9). Additionally, this compound also prevents TPA-induced tumor formation. In other animal models, shogaol decreases expression of iNOS, IL-1β, and TNF-α, preventing ulcer formation. Shogaol also inhibits 5-HT3 receptors, activates PPARγ, and decreases capsaicin-induced release of substance P.