Description
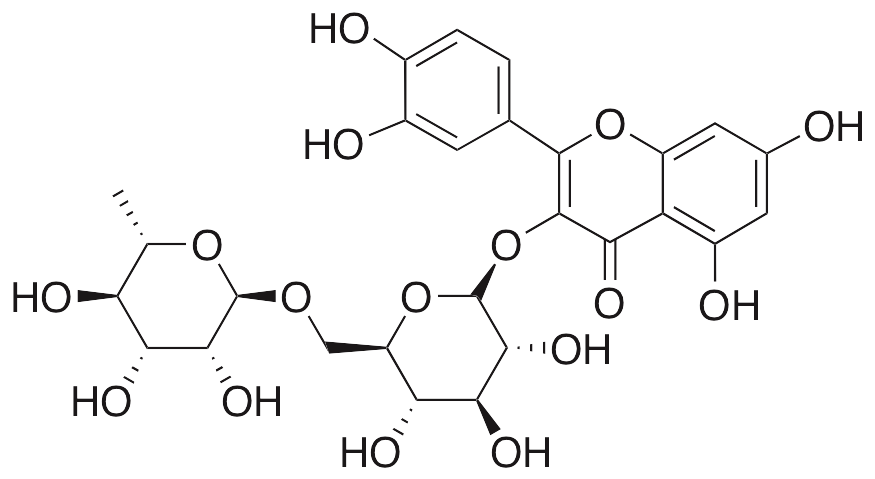
Rutin is a flavonoid glycoside found in rhubarb, asparagus, buckwheat, citrus, and berries; it exhibits anxiolytic, antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, anti-obesity, anti-diabetic, and neuroprotective activities. In animal models of restraint stress, rutin decreases locomotor activity, oxidative stress, and cortisone levels. In animal models of acute lung injury, rutin inhibits granulocyte infiltration, increases expression of catalase, superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase, and heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1), decreases inflammatory cytokine secretion and lipid peroxidation, and suppresses activation of MAPKs and NF-κB. Rutin increases glucose uptake in a PI3K- and PKC-dependent manner; it also increases insulin secretion and prevents fatty liver disease and obesity in animal models. In neurons, rutin protects against 6-OHDA-induced toxicity. In animal models of Alzheimer’s disease, this compound ameliorates cognitive deficits.