Description
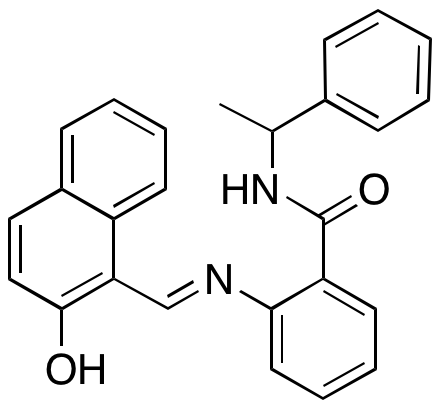
Sirtinol is a sirtuin inhibitor and iron chelator that exhibits antiviral, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and anti-angiogenic activities. In vivo, sirtinol induces apoptosis-like changes in platelets, decreasing platelet count. In vitro, this compound decreases levels of hepatitis A virus RNA by suppressing translation and replication. Sirtinol also induces apoptosis in lung cancer cells by increasing levels of ROS. In other cellular models, sirtinol disrupts oocyte polarity and actin cap formation, preventing meiosis. In mesenchymal stem cells, this compound decreases tube formation and cell migration. Additionally, sirtinol also increases nasal polyp development and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in vitro and in vivo. In animal models, sirtinol decreases paw edema.