Description
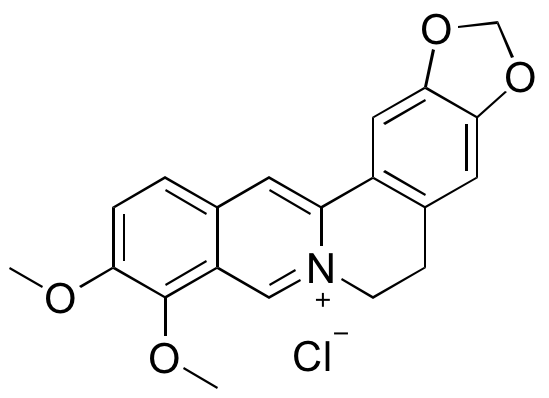
Berberine is an isoquinoline alkaloid found in a variety of plants, including barberry, goldenseal, Oregon grape, California poppy, and the Amur cork tree. Berberine fluoresces under ultraviolet light and is often used to stain heparin in mast cells. Berberine displays many beneficial effects, including immunomodulatory, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, lipid-lowering, and antidepressant activities. This compound is a competitive inhibitor of both acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and prolyl oligopeptidase, enzymes important in neuropsychiatric disorders such as Alzheimer’s Disease, depression, schizophrenia, and anxiety. In animal models of depression, berberine increases levels of 5-HT, DA, and NE and is also thought to act on σ receptors. Berberine suppresses hedgehog (Hh) signaling, likely through inhibition of the Smoothened (Smo) receptor.