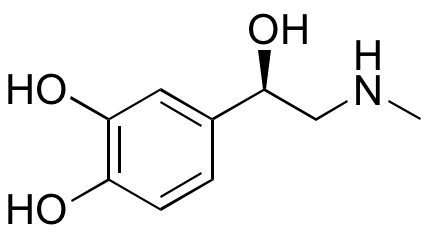
Description
(-)-Epinephrine is the active isomer of epinephrine, an endogenous hormone neurotransmitter. Epinephrine exhibits bronchodilatory, vasoconstrictive and cardiostimulantory/positive inotropic activities. Epinephrine acts as a non-selective agonist at both α- and β-adrenergic receptors, activating the sympathetic nervous system. Epinephrine is clinically used to treat cardiac arrest and anaphylaxis, as it increases cardiac output and peripheral resistance and decreases edema by suppressing leakage from constricted vessels. This compound also inhibits insulin secretion, increases glucagon and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) secretion, and induces glycogenolysis, glycolysis, and lipolysis to increase energy production.