Description
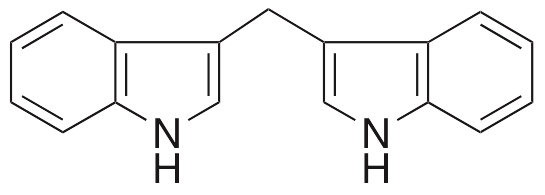
3,3’-Diindolylmethane (DIM) is found in cruciferous vegetables; it exhibits anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive, antioxidative, anti-diabetic, anti-fibrotic, anti-metastatic, anticancer chemotherapeutic, and chemopreventive activities. DIM acts as an agonist at the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. DIM increases levels of Foxp3 and function of Treg cells and decreases expression of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and Th17 cells, preventing hepatic steatosis and inflammation in vivo. DIM also prevents the development of experimental autoimmune encephalitis (EAE) by suppressing T cell activity. In vivo, this compound decreases glucose levels, insulin levels, and Hb1Ac by increasing activity of glucokinase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and decreasing activity of glucose-6-phosphatase and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. DIM also prevents the development of liver fibrosis in vivo. In cellular and animal models of nasopharyngeal carcinoma, DIM inhibits cellular invasion and metastasis and tumor growth; it also decreases activity of HDAC2.