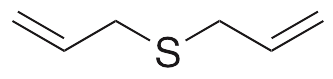
Description
Diallyl sulfide is an organosulfur initially found in garlic; it exhibits anticancer chemotherapeutic, chemopreventive, neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, anti-angiogenic, and anti-metastatic activities. Diallyl sulfide decreases DES-induced DNA damage and carcinogenesis in vitro and in vivo; it also inhibits the development of colon polyps in other carcinogenesis models. In animal models of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion, diallyl sulfide decreases infarct volume, apoptosis, and caspase 3 activation and increases levels of Bcl-2. In vitro, this compound decreases TNF-α-induced activation of NF-κB and suppresses histamine-induced levels of ROS, IL-1β, and TNF-α. Like other organosulfurs, diallyl sulfide induces phase II enzymes, increasing glutathione-S-transferase, glutathione reductase, superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase, and Nrf2 in vivo. In animal models of osteosarcoma, diallyl sulfide decreases VEGF levels, microvessel density, cellular invasion, and tumor growth.