Description
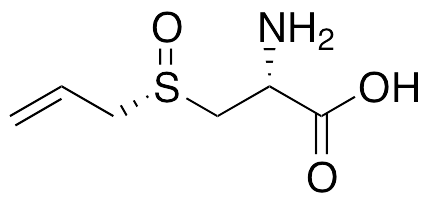
L-(+)-Alliin is a cysteine derivative originally found in Allium sativum (garlic); it exhibits anti-inflammatory, neuromodulatory, anti-diabetic, anti-hyperlipidemic, antioxidative, cardioprotective, and anti-angiogenic activities; it is the optically active and orally bioavailable isomer of alliin. In adipocytes, it inhibits LPS-stimulated activation of ERK1/2 and increases in inflammatory signaling. In animal models of myocardial infarction, it increases activity of superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase, catalase, and glutathione-S-transferase. L-Alliin also activates NMDA-R subunits NR2A and NR2B. In diabetic rats, this compound decreases levels of LDL, VLDL, glucose, triglycerides, total cholesterol, and total lipids. Additionally, it inhibits VEGF-induced angiogenesis and FGF2 and VEGF secretion in fibrosarcoma cells.