Description
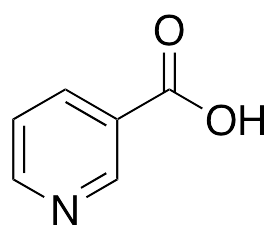
Niacin is a water-soluble vitamin of the B complex occurring in various animal and plant tissues; it is required by the body for the formation of coenzymes NAD and NADP. Niacin displays anti-dyslipidemic and cardioprotective properties, although various studies show mixed benefits in vivo and in clinical settings. Niacin binds to the G-protein coupled receptor 109A (GPR109A), increasing arachidonic acid levels and prostaglandin synthesis and signaling, resulting in cutaneous vasodilation and flushing. Niacin decreases surface expression of hepatic ATP synthase β, decreasing catabolism of HDL and increasing serum HDL levels. Additionally, niacin inhibits hepatic diacylglycerol acyltransferase-2, inhibiting synthesis of triglyceride and decreasing apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins; this results in decreased secretion of VLDL and LDL.