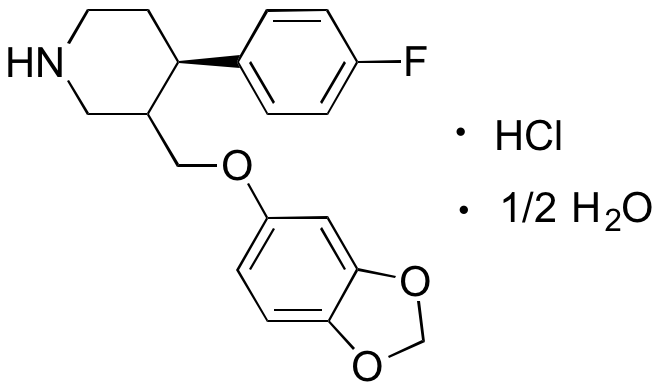
Description
Paroxetine is a SSRI that primarily inhibits activity of the 5-HT transporter (SERT) but also displays some affinity for the norepinephrine transporter (NET) and for muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs). Paroxetine exhibits antidepressant, antibiotic, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective activities. This compound displays antibacterial efficacy against gram positive bacteria and antifungal efficacy against Aspergillus and Candida. In vitro, paroxetine inhibits LPS-induced production of iNOS, TNF-α, and IL-1β and suppresses activation of JNK1/2 and microglia. Additionally, paroxetine decreases amyloid-β (Aβ) oligomer levels when administered clinically to subjects with Alzheimer’s disease. This compound also acts as a functional inhibitor of acid sphingomyelinase (FIASMA).