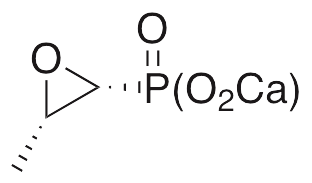Description
Fosfomycin is an antibiotic initially produced by Streptomyces that exhibits antibacterial, anti-parasitic, antimalarial, and nephroprotective activities. Fosfomycin is active against both gram positive and gram negative bacteria and acts by inhibiting MurA and preventing synthesis of bacterial cell walls. Fosfomycin also inhibits isopentenyl phosphate kinase, an enzyme in the archaeal mevalonate pathway. In vivo, fosfomycin inhibits iron release from the mitochondria, inhibiting lipid peroxidation and preventing aminoglycoside antibiotic-induced nephrotoxicity. This compound also displays some anti-inflammatory benefit, decreasing serum levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 in animal models of septic Pseudomonas infection, increasing survival rates.