Description
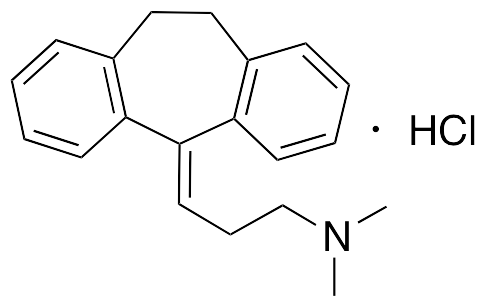
Amitriptyline exhibits antidepressant, antipsychotic, analgesic, and antinociceptive activities; it acts as an antagonist at 5-HT2A/2C/6/7 receptors, M1-5 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs), H1/4 histamine receptors, α1-adrenergic receptors, and also on the serotonin transporter (SERT) and norepinephrine transporter (NET). Additionally, amitriptyline acts as an agonist at σ1 receptors and TrkA/B receptors. Amitriptyline inhibits shaker-related Kv1.1 (KCNA1), Kv7.2 (KCNQ2), and Kv7.3 (KCNQ3) voltage-gated K+ channels and L-type voltage-gated Ca2+ channels; it inhibits expression of Nav1.1 (SCN1A) and Nav1.2 (SCN2A) voltage-gated Na+ channels and activates ryanodine RyR2 receptors. Amitriptyline also decreases levels of α1-adrenergic receptors in the cortex and cerebellum in vivo. In animal models of chronic constrictive injury and neuropathic pain, amitriptyline decreases thermal hyperanalgesia. In PC12 neurons, this compound exhibits neuroprotective activity, increasing neurite outgrowth and decreasing cell death. Amitriptylene is also a function inhibitor of acid sphingomyelinase (FIASMA).