Description
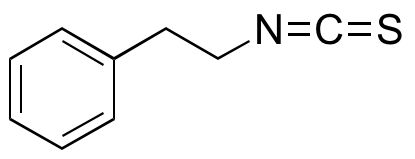
Phenethyl isothiocyanate (PEITC) is found in plants of the Brassicaceae family, including broccoli, cabbage, and radish. Isothiocyanates are best known for their antioxidative, anticancer chemotherapeutic, chemopreventive, anti-angiogenic, and antibiotic properties. In vitro, PEITC increases caspase 3 activity and cleavage of poly(ADP)-ribose polymerase (PARP), inducing caspase-mediated apoptosis in Jurkat T cells and other cellular models. PEITC increases activation of JNK1, one potential mechanism behind its regulation of phase II detoxifying enzyme gene expression. Additionally, PEITC decreases levels of Bcl-xl and increases levels of Bax, also decreasing the mitochondrial membrane potential and inducing intracellular influx of free Ca2+, resulting in cell death. This compound decreases oxidation of carcinogen NNK and increases activity of NADPH:quinone oxidoreductase and glutathione S-transferase in vitro and in vivo. In glioma cells, PEITC alters PI3K/MAPK signaling to inhibit accumulation of HIF-1α and secretion of VEGF during hypoxia.
Refractive index:n20/D 1.5888(lit.)